By STMicroelectronics 180
LSM6DSOXTR is a Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) sensor commonly used to measure and monitor the motion, acceleration, angular velocity and attitude of objects. This device is manufactured by STMicroelectronics as part of its product family.
MEMS sensors are miniature electromechanical systems that are capable of detecting and measuring physical quantities such as acceleration, angular velocity, position, and pressure. These sensors are widely used in various fields, including automotive, medical, consumer electronics, and industrial automation.
LSM6DSOX meets mainstream OS requirements and provides 9 KB of batch data for various types of sensors, including real, virtual, and batch. STMicroelectronics' MEMS sensor modules use a reliable, proven production process and have been widely used in miniature accelerometers and gyroscopes. Different types of sensitive components are produced through special micro-machining processes, and the IC interface is developed using the CMOS process, allowing special circuits to be designed and better matched with the performance of the sensing components.

Ⅰ.Working principle of LSM6DSOXTR
1.Three-axis accelerometer: The accelerometer part of the LSM6DSOXTR uses a microelectromechanical system (MEMS) mass block and a microelectronic sensor to measure the linear acceleration of an object. When an object is accelerated, the mass undergoes small displacements, and the sensor detects these displacements. By measuring these displacements and applying Newton's second law, the acceleration of an object can be calculated. These acceleration values are usually output in digital form.
2.Data acquisition method: LSM6DSOXTR transmits accelerometer and gyroscope data to a microcontroller or other processor through a digital interface (usually I2C or SPI). The processor can periodically poll sensor data on demand, or the sensor can be configured to trigger data collection when a specific event occurs, such as movement, vibration, or rotation.
3.Three-axis gyroscope: The gyroscope part uses a gyroscope sensor to measure the angular velocity of the object, that is, the rotation speed of the object. When an object rotates about any axis, the rotating part of the gyroscope senses changes in angular velocity. This change is converted into digital signals to provide the object's rotational speed around the X, Y and Z axes.
4.Data fusion: In some applications, LSM6DSOXTR can fuse accelerometer and gyroscope data to calculate the attitude or direction of an object. This process, often called sensor fusion, can provide more accurate attitude information, especially in complex motion situations.
Ⅱ.Specification parameters of LSM6DSOXTR
•Number of pins:14
•Installation style:SMD/SMT
•Package/Box:LGA-14L
•Sensor type:6-axis
•Interface type:Serial
•Output type:Digital
•Acceleration:2g,4g,8g,16g
•Resolution:16 bit
•Sensitivity:0.488 mg/LSB
•Minimum operating temperature:-40℃
•Minimum operating temperature:+85℃
•Supply voltage-minimum:1.71 V
•Supply voltage-Max:3.6 V
•Operating power supply current:550 uA
•Packaging:Cut Tape
•Trademark:STMicroelectronics
Ⅲ.Pin description of LSM6DSOXTR
The LSM6DSOX offers flexibility to connect the pins in order to have four different mode connections and functionalities. In detail:
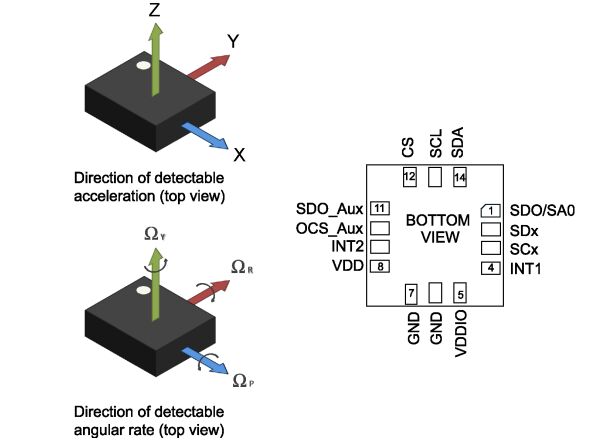
•Mode 1: I²C / MIPI I3CSM slave interface or SPI (3-and 4-wire) serial interface is available;
•Mode 2: I²C / MIPI I3CSM slave interface or SPI (3-and 4-wire) serial interface and I2C interface master for external sensor connections are available;
•Mode 3: I²C / MIPI I3CSM slave interface or SPI (3-and 4-wire) serial interface is available for the application processor interface while an auxiliary SPI (3- and 4-wire) serial interface for external sensor connections is available for the gyroscope ONLY;
•Mode 4: I²C / MIPI I3CSM slave interface or SPI (3- and 4-wire) serial interface is available for the application processor interface while an auxiliary SPI (3- and 4-wire) serial interface for external sensor connections is available for the accelerometer and gyroscope.
Ⅳ.Application scope of LSM6DSOXTR
1.Smartphones and smart watches: The LSM6DSOXTR sensor can be used to detect the movement, direction and attitude of devices such as smartphones and smart watches. By measuring acceleration and angular velocity, the sensor can provide information about the device's motion, enabling features such as screen rotation, gesture control, and pedometers. In smartphones and smartwatches, the LSM6DSOXTR sensor can detect the motion and orientation of the device to control screen rotation and automatically adjust screen orientation. In addition, it can also be used to monitor the posture of the device, such as monitoring the bending of the wrist in smart watches, to control the brightness and display content of the screen.
2.Sports and health tracker: LSM6DSOXTR is also used to measure the user's steps, distance, calorie consumption and sleep quality to support health and sports tracking applications.
3.Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR): Using LSM6DSOXTR in headsets and handles can track the user's head and hand movements in real time, providing a more realistic virtual experience.
4.Self-driving cars: In self-driving cars, LSM6DSOXTR is used to monitor the movement and attitude of the vehicle to help the vehicle perceive the surrounding environment and make driving decisions.
5.Navigation and Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Using the LSM6DSOXTR in GPS and navigation devices can help determine the device's direction and acceleration, providing more accurate location and navigation information.
6.Aircraft and drones: In aircraft and drones, LSM6DSOXTR can be used for stabilization and navigation, helping them maintain balance and direction.
7.Self-driving cars: In self-driving cars, LSM6DSOXTR is used to monitor the movement and attitude of the vehicle to help the vehicle perceive the surrounding environment and make driving decisions.
8.Somatosensory game control: Using LSM6DSOXTR in a game controller can capture the player's movements and gestures to achieve more intuitive game control.
9.Industrial automation: In factory automation and robots, LSM6DSOXTR can be used to monitor the position, vibration and attitude of machines to improve production efficiency and safety.
Ⅴ.Embedded low power consumption features of LSM6DSOXTR
The LSM6DSOX has been designed to be fully compliant with Android, featuring the following on-chip functions:
•9 kbytes data buffering, data can be compressed two or three times
-Possibility to store timestamp
-100% efficiency with flexible configurations and partitioning
•Specific IP blocks with negligible power consumption and high-performance
-Tilt
-Significant Motion Detection
-Pedometer functions: step detector and step counters
-Machine Learning Core (MLC)
-Finite State Machine (FSM) for accelerometer, gyroscope, and external sensors
•Event-detection interrupts (fully configurable)
-Wakeup
-Free-fall
-6D orientation
-Activity/Inactivity recognition
-Click and double-click sensing
Ⅵ.LSM6DSOXTR communicates
•LSM6DSOXTR supports two main communication protocols:
1.SPI interface: SPI is another serial communication protocol usually used for high-speed data transmission. To communicate with the LSM6DSOXTR using SPI, you need to connect the device's SPI pins (usually SCK, MISO, MOSI, and CS) to the target system's SPI bus. You can then read and write the LSM6DSOXTR register via the SPI protocol.
2.I2C interface: I2C is a common serial communication protocol used to connect multiple devices. To communicate with the LSM6DSOXTR using I2C, you need to connect the device's I2C pins (usually SDA and SCL) to the target system's I2C bus. You can then use the target system's programming language or library to read and write the LSM6DSOXTR's registers to obtain sensor data or configure the sensor.
•Communication steps:
1.Initialize the communication interface: Determine the communication interface you want to use (I2C or SPI), and connect the sensor to the target system.
2.Configure the sensor: Configure the sensor to meet your application needs by writing to the register of LSM6DSOXTR, such as setting the sampling rate, range, trigger conditions, etc.
3.Read data: Read data from the sensor as needed, this can be done by reading the register of LSM6DSOXTR.
4.Process the data: Once the sensor data is acquired, you can process and interpret the data to meet your application needs.
Ⅶ.Mechanical properties of LSM6DSOXTR

Ⅷ.Similar models of LSM6DSOXTR
1.MPU6050: MPU6050 is a six-axis sensor with a three-axis accelerometer and a three-axis gyroscope. It is a sensor commonly used for attitude detection and motion tracking.
2.BMI160: The BMI160 is a low-power six-axis sensor suitable for portable devices, smartphones and health trackers. It has a three-axis accelerometer and a three-axis gyroscope.
3.MPU9250: MPU9250 is another six-axis sensor that also includes a three-axis accelerometer, a three-axis gyroscope, and a three-axis magnetometer. It can be used in a wider range of applications, including indoor navigation and magnetic field positioning.
4.L3GD20: L3GD20 is a three-axis gyroscope produced by STMicroelectronics. It is used to measure the angular velocity of objects and is suitable for fields such as navigation, autonomous driving, and virtual reality.
5.BNO055: BNO055 is a nine-axis sensor with a three-axis accelerometer, a three-axis gyroscope and a three-axis magnetometer. It can provide more accurate attitude and direction information and is suitable for fields such as virtual reality, AR, and indoor navigation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.How does the LSM6DSOXTR sensor measure acceleration and angular velocity?
Measuring acceleration: The sensor contains tiny mass blocks inside, which can vibrate freely on three axes; when the sensor is subjected to external acceleration, these mass blocks will undergo slight displacements and follow the external movement. Measuring angular velocity: A gyroscope measures angular velocity by detecting changes in the angle of a mass, often using changes in capacitance or other sensing mechanisms; angular velocity is usually measured in degrees/second or radians/second.
2.What is the difference between LSM6DSOXTR and other sensors?
LSM6DSOXTR is a six-axis sensor with both a three-axis accelerometer and a three-axis gyroscope. This versatility makes it suitable for applications that require simultaneous measurement of acceleration and angular velocity without having to use two separate sensors. LSM6DSOXTR typically has high performance characteristics, including higher sampling rates, low noise levels, and high accuracy. This gives it a competitive advantage in applications that require high-precision measurements, such as virtual reality and navigation systems.
3.What is the LSM6DSOXTR sensor used for?
The LSM6DSOXTR sensor is used to measure both linear acceleration (through its accelerometer) and angular velocity (using its gyroscope) in various applications.
4.Can the LSM6DSOXTR sensor be integrated into battery-powered devices?
Yes, the LSM6DSOXTR sensor typically features low-power modes, making it suitable for integration into battery-powered devices to extend battery life.